PCL1
SRR 14708246
General Information
- Accession Date
- May 31, 2021
- Reported Plant Sex
- not reported
- Report Type
- Whole-Genome Sequencing
The strain rarity visualization shows how distant the strain is from the other cultivars in the Kannapedia database. The y-axis represents genetic distance, getting farther as you go up. The width of the visualization at any position along the y-axis shows how many strains there are in the database at that genetic distance. So, a common strain will have a more bottom-heavy shape, while uncommon and rare cultivars will have a visualization that is generally shifted towards the top.
Chemical Information
Cannabinoid and terpenoid information provided by the grower.
Cannabinoids
No information provided.
Terpenoids
No information provided.
Genetic Information
- Plant Type
- Type II
File Downloads
The bell curve in the heterozygosity visualization shows the distribution of heterozygosity levels for cannabis cultivars in the Kannapedia database. The green line shows where this particular strain fits within the distribution. Heterozygosity is associated with heterosis (aka hybrid vigor) but also leads to the production of more variable offspring. When plants have two genetically different parents, heterozygosity levels will be higher than if it has been inbred or backcrossed repeatedly.
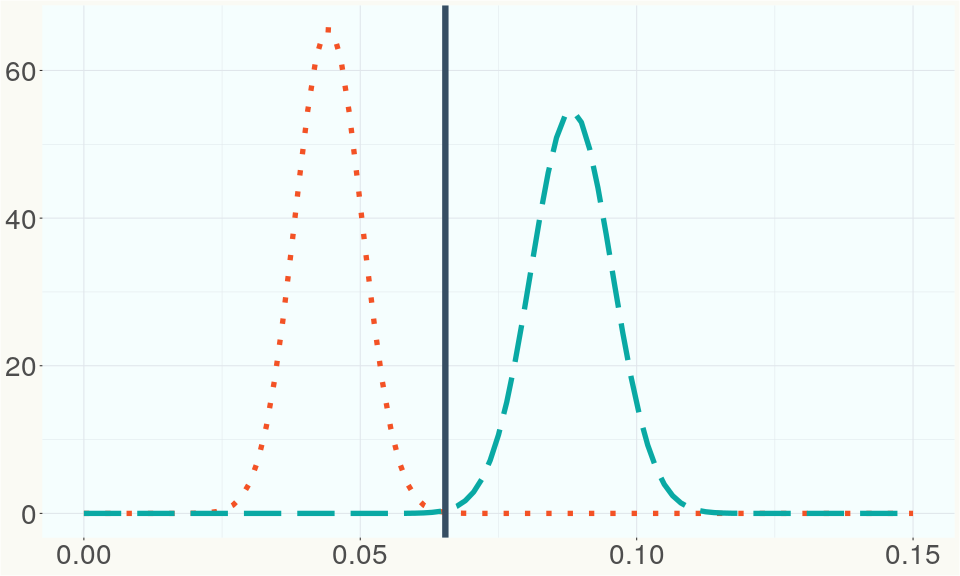
The ratio of reads mapped to Y-contigs to reads mapped to the whole Cannabis genome (Y-ratios) has been demonstrated to be strongly correlated with plant sex typing. This plot shows the distribution of Y-ratios for all samples in our database which were sequenced with the same method (panel or WGS) as this sample and where this sample falls in the distribution.
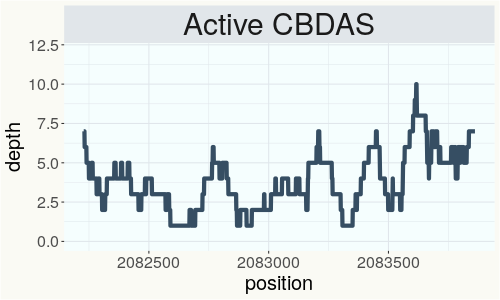
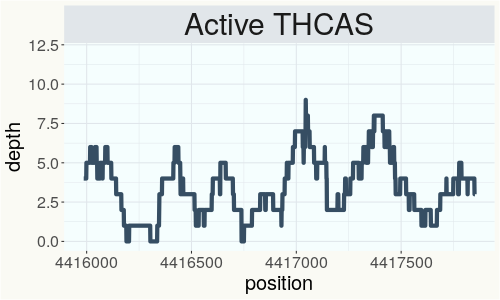
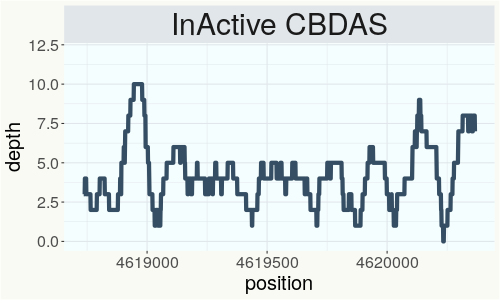
This chart represents the Illumina sequence coverage over the Bt/Bd allele. These are the three regions in the cannabis genome that impact THCA, CBDA, CBGA production. Coverage over the Active CBDAS gene is highly correlated with Type II and Type III plants as described by Etienne de Meijer. Coverage over the THCA gene is highly correlated with Type I and Type II plants but is anti-correlated with Type III plants. Type I plants require coverage over the inactive CBDA loci and no coverage over the Active CBDA gene. Lack of coverage over the Active CBDA and Active THCA allele are presumed to be Type IV plants (CBGA dominant). While deletions of entire THCAS and CBDAS genes are the most common Bt:Bd alleles observed, it is possible to have plants with these genes where functional expression of the enzyme is disrupted by deactivating point mutations (Kojoma et al. 2006).
This chart represents the Illumina sequence coverage over the CBCA synthase gene.
Variants (THCAS, CBDAS, and CBCAS)
No variants to report
Variants (Select Genes of Interest)
| aPT1 | c.629C>T | p.Thr210Ile | missense variant | moderate | contig121 | 2840237 | C/T | |
| AAE1-2 | c.331A>G | p.Asn111Asp | missense variant | moderate | contig81 | 209293 | A/G |
|
| AAE1-2 | c.1006A>G | p.Lys336Glu | missense variant | moderate | contig81 | 209968 | A/G |
|
| HDS-1 | c.136G>A | p.Val46Ile | missense variant | moderate | contig1891 | 889256 | C/T | |
| aPT4 | c.202T>A | p.Leu68Ile | missense variant | moderate | contig121 | 2828858 | T/A |
|
| aPT4 |
c.235_236del |
p.Val79fs | frameshift variant | high | contig121 | 2829030 | ATG/A |
|
| aPT4 | c.238delT | p.Ser80fs | frameshift variant | high | contig121 | 2829034 | AT/A |
|
Nearest genetic relatives (All Samples)
- 0.166 PCL2 (SRR14708245)
- 0.252 KYRG-151 (RSP11052)
- 0.254 PID2 (SRR14708247)
- 0.255 Jiangji (RSP10653)
- 0.258 IBR2 (SRR14708250)
- 0.259 Tisza (RSP10659)
- 0.261 PID1 (SRR14708248)
- 0.261 Tak-HN (RSP11618)
- 0.264 IBR3 (SRR14708249)
- 0.264 IBE (SRR14708228)
- 0.265 R3 (RSP11616)
- 0.266 KYRG-11 (RSP11051)
- 0.266 Santhica27 (RSP10056)
- 0.267 Tisza (RSP11044)
- 0.267 IUL3 (SRR14708252)
- 0.267 R2 (RSP11615)
- 0.269 IBR1 (SRR14708251)
- 0.269 IMA (SRR14708203)
- 0.269 YNN (SRR14708199)
- 0.269 VIR 369 (SRR14708231)
Most genetically distant strains (All Samples)
- 0.458 Cherry Blossom (RSP11318)
- 0.442 Cherry Blossom (RSP11323)
- 0.440 Cherry Blossom (RSP11300)
- 0.436 Cherry Blossom (RSP11328)
- 0.435 Cherry Blossom (RSP11301)
- 0.434 Unknown--Cherry Wine---001- (RSP11268)
- 0.429 Cherry Blossom (RSP11331)
- 0.427 Cherry Blossom (RSP11311)
- 0.427 Chem 91 (RSP11185)
- 0.427 Cherry Blossom (RSP11312)
- 0.424 GG4 (RSP11978)
- 0.422 Cherry Blossom (RSP11333)
- 0.420 Cherry Blossom (RSP11306)
- 0.420 Cherry Blossom (RSP11322)
- 0.420 QLE1 (RSP11451)
- 0.418 New York City Deisel (RSP11225)
- 0.418 RKM-2018-002 (RSP11093)
- 0.418 CHEM4 (RSP12090)
- 0.417 Cherry Blossom (RSP11302)
- 0.415 Cherry Blossom (RSP11329)
Nearest genetic relative in Phylos dataset
- Overlapping SNPs:
- 8
- Concordance:
- 7